A thorough approach for addressing the specific needs of women
As dedicated healthcare practitioners, we understand the vital importance of staying up-to-date with the latest advancements and knowledge in this field. Our goal is to equip you with a information and valuable resources that can enhance your understanding and support your practice when it comes to women's hormonal health.
Hormonal health
Throughout the lifecycle, women are affected by the fluctuation of hormones. The body addresses these fluctuations in order to maintain harmonious equilibrium. However, there are lifestyle factors that can influence hormonal balance and affect a variety of general and sex-specific functions for women.
The influence of nutrition and modern living on hormone metabolism
Nutrition plays a significant role in estrogen metabolism as it affects its mechanism of action. Fat-soluble vitamins A and E, as well as water-soluble vitamins B2, B6, and B12, are key in this metabolism process.
Influences such as poor diet, obesity, and excess alcohol consumption, as well as overexposure to pesticides and industrial chemicals, can negatively influence the production of estrogen. Examples of how estrogen dysregulation manifests include difficulty losing weight when levels are elevated, or weight gain when too little estrogen is produced. Additionally, the stress of modern living and compressed work and family schedules can compound any issues that the body has with hormone metabolism. For example, the natural “fight or flight” response to stress, when sustained over a period of time, can impact normal processes pertaining to reproductive organs such as menstrual regularity, as well as other glands within the endocrine system.
Throughout the lifecycle, women are affected by the fluctuation of hormones. The body addresses these fluctuations in order to maintain harmonious equilibrium. However, there are lifestyle factors that can influence hormonal balance and affect a variety of general and sex-specific functions for women.
The influence of nutrition and modern living on hormone metabolism
Nutrition plays a significant role in estrogen metabolism as it affects its mechanism of action. Fat-soluble vitamins A and E, as well as water-soluble vitamins B2, B6, and B12, are key in this metabolism process.
Influences such as poor diet, obesity, and excess alcohol consumption, as well as overexposure to pesticides and industrial chemicals, can negatively influence the production of estrogen. Examples of how estrogen dysregulation manifests include difficulty losing weight when levels are elevated, or weight gain when too little estrogen is produced. Additionally, the stress of modern living and compressed work and family schedules can compound any issues that the body has with hormone metabolism. For example, the natural “fight or flight” response to stress, when sustained over a period of time, can impact normal processes pertaining to reproductive organs such as menstrual regularity, as well as other glands within the endocrine system.
Supporting balance through targeted nutrition
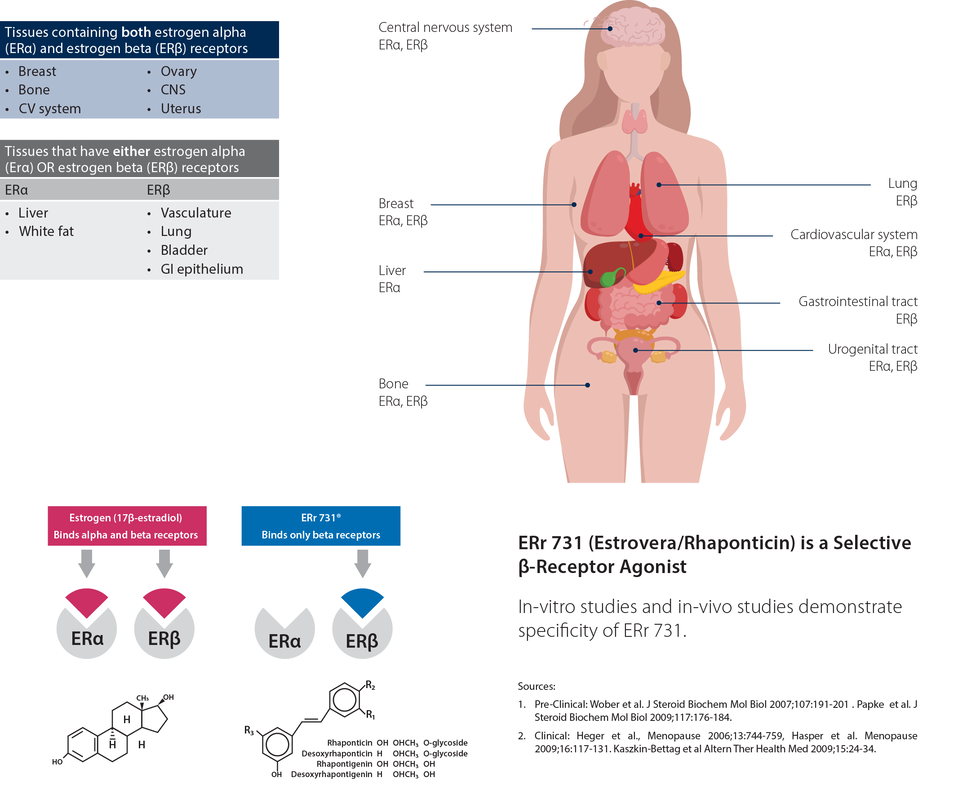
Estrogen receptors are present in various tissues throughout the body. Endogenous estrogens, environmental xenoestrogens, and their metabolites selectively bind to estrogen receptors, thereby influencing estrogen balance. Various phytonutrients may moderate this binding process and reduce or moderate cell signaling to promote hormone balance. Examples include lignans, isoflavones and ErR 731. ErR 731, a non-hormonal selective ERB agonist that preferentially binds to ERB, has been found to provide multiple systemic benefits including vascular relaxation and tissue protective effects.
Estrogen is a unique hormone with both alpha and beta receptors and found in many tissues of the body
Estrogen receptors are present in various tissues throughout the body. Endogenous estrogens, environmental xenoestrogens, and their metabolites selectively bind to estrogen receptors, thereby influencing estrogen balance. Various phytonutrients may moderate this binding process and reduce or moderate cell signaling to promote hormone balance. Examples include lignans, isoflavones and ErR 731. ErR 731, a non-hormonal selective ERB agonist that preferentially binds to ERB, has been found to provide multiple systemic benefits including vascular relaxation and tissue protective effects.
Estrogen is a unique hormone with both alpha and beta receptors and found in many tissues of the body
Addressing the specific needs of women
Certain nutritional approaches have been studied for how they interplay with hormone pathways. Metagenics builds upon this science to offer an extensive line of nutritional formulas that target specific support areas for women’s hormonal health.
Certain nutritional approaches have been studied for how they interplay with hormone pathways. Metagenics builds upon this science to offer an extensive line of nutritional formulas that target specific support areas for women’s hormonal health.
|
Join Our Community
|
|
Amipro Disclaimer:
Certain persons, considered experts, may disagree with one or more of the foregoing statements, but the same are deemed, nevertheless, to be based on sound and reliable authority. No such statements shall be construed as a claim or representation as to Metagenics products, that they are offered for the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of any disease. |